Mitigation - How to Fix a Radon Problem - Iowa Department of


National Radon Defense Midwest - Radon Mitigation System - Manometer of a Depressurization Radon Mitigation System in Superior, NE
The Ultimate Guide To What is Radon Mitigation?
Any procedure utilized to decrease radon gas concentrations in the breathing zones of occupied buildings, or radon from water products Radon mitigation is any process used to decrease radon gas concentrations in the breathing zones of occupied buildings, or radon from water supplies. Radon is a considerable factor to ecological radioactivity. Mitigation of radon in the air is achieved through ventilation, either collected below a concrete floor piece or a membrane on the ground, or by increasing the air modifications per hour in the building. More In-Depth using aeration or triggered charcoal are readily available to remove radon from domestic water materials.

Radon: Your Uninvited, Unseen & Unwanted House Guest - The Navage Patch
Change of ambient air radon concentration over one week, determined in a laboratory The very first action in mitigation is testing to see if the indoor-air and/or domestic water radon concentrations should be minimized. No level of radiation is thought about completely safe, but it can not be absolutely removed so governments all over the world have actually set various action levels to offer guidance on when radon concentrations ought to be reduced. The World Health Company's International Radon Task has suggested an action level of 100 Bq/m3 (2. 7 p, Ci/ l) for radon in the air. Radon in the air is considered to be a bigger health risk than radon in domestic water so the US Epa recommendation is to not test for radon in water unless a radon in air test is above the action level.
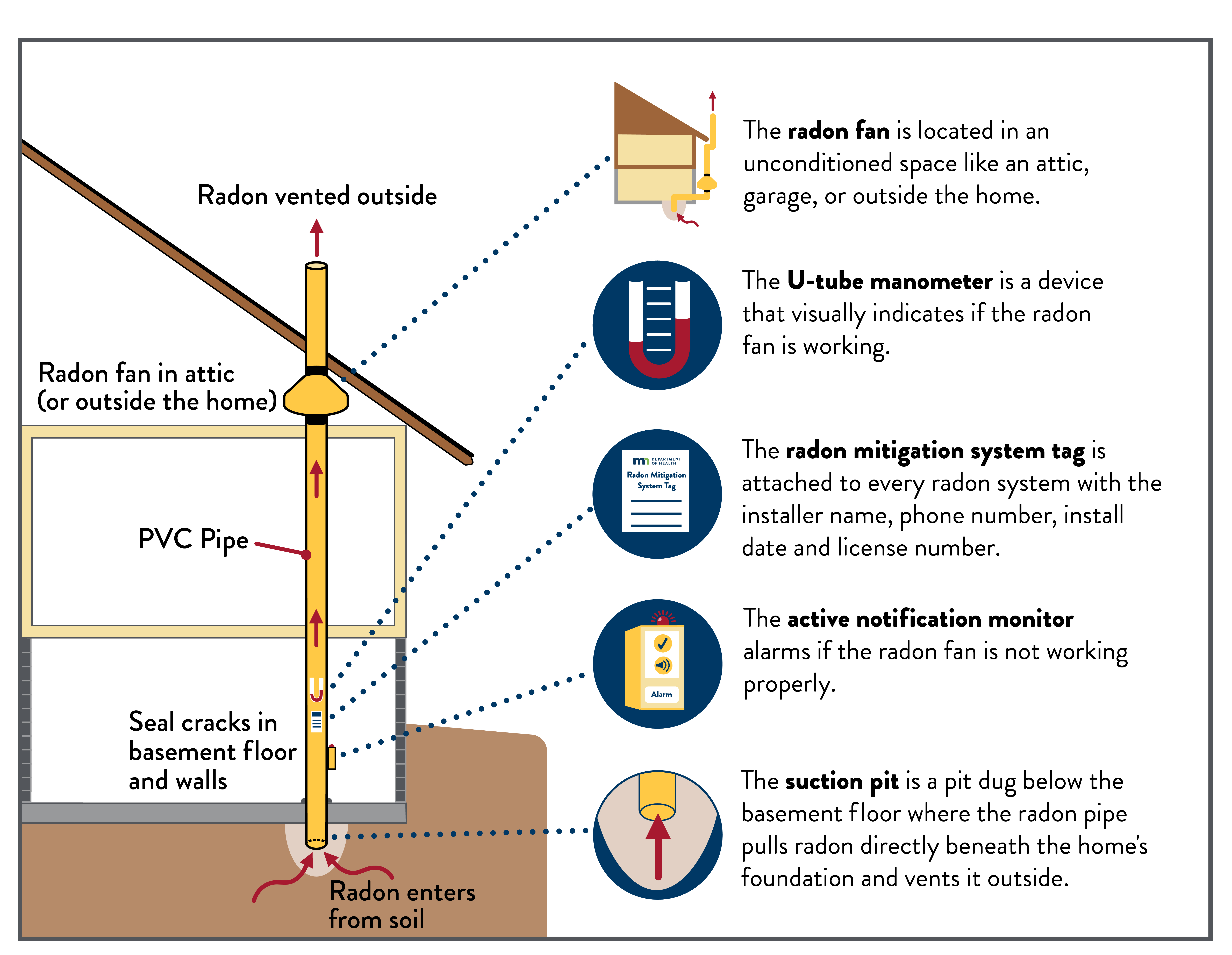
Waukesha Radon Mitigation Install - Lifetime Radon Solutions Delafield, Wisconsin
The US government has not set an action level for radon in water. Air-radon levels change naturally on an everyday and seasonal basis. A brief term test (90 days or less) may not be an accurate evaluation of a house's typical radon level, but are recommended for preliminary testing to quickly determine unhealthy conditions. Short-term weather such as wind and modifications in barometric pressure can impact short-term concentrations in addition to ventilation such as open windows and the operation of exhaust fans. Evaluating for radon in the air is accomplished using passive or active devices positioned in the building. Some gadgets are quickly sent out to a lab for analysis, others determine the results on-site.

